Electrical cabinets of various purposes usually hold different type of electrical components like fuse, AC/DC converter, switch, LED. They provide protection for the sophisticated equipment against extreme environmental condition, humidity, water infiltration, dust accumulation and physical damages in various industrial environment. But the insulated protective enclosures that provide mechanical support while preventing water and dust infiltration, also degrade thermal dissipation characteristics. The resulting poor thermal properties may lead to overheating failure of electrical components as a form of burning, thermal deformation during elevated environmental temperature under extreme conditions. Therefore, it is necessary to design and certify the electrical systems considering the maximum operable temperature condition, while pursuing design improvement through a combination of extensive testing and thermal simulation. A collaboration project was developed between Palazzoli SpA and m4lab at the University of Brescia to meet the challenge and improve the solution that can prevent overheating failure for high power application.
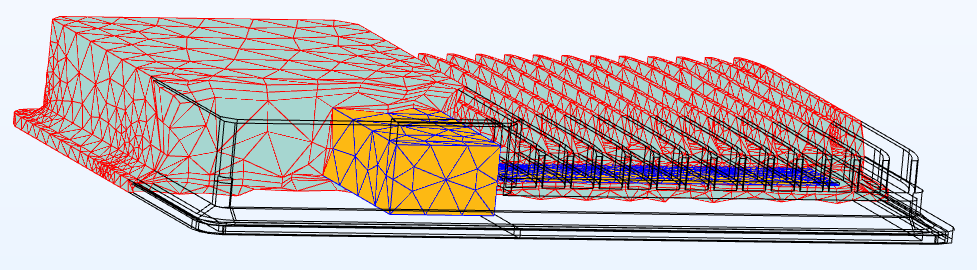
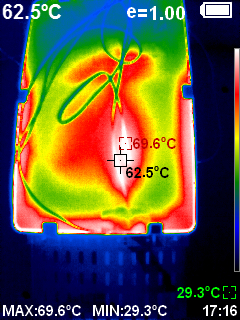
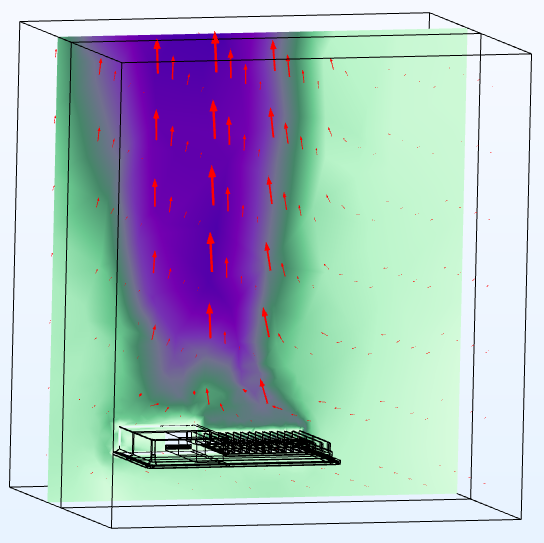
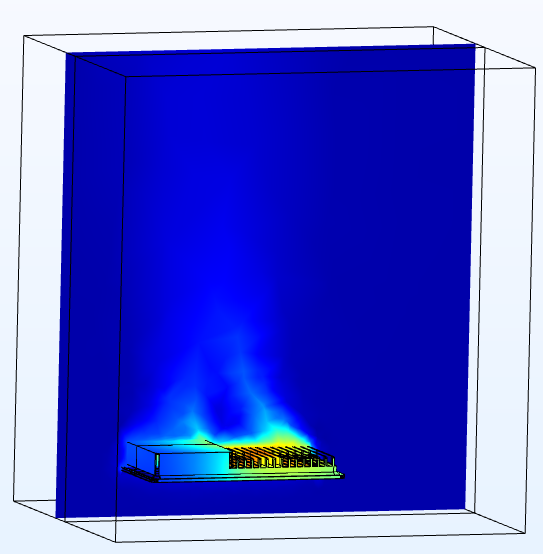
COMSOL Multiphysics has been used to numerically simulate the thermal behavior of various electrical cabinets under versatile environmental conditions. The fluid dynamics has been coupled with thermal conduction and radiation to capture the thermal properties of the electrical systems made of Glass Reinforced Plastic and Aluminum. Thermocouple sensors and thermographic camera were used to measure thermal profile of various electrical systems. Thermal simulation by COMSOL Multiphysics allowed a profound understanding of the internal physics. It has been observed that natural air convection, conductivity of enclosure material, and radiative surface plays a role in thermal dissipation depending on the sizes of enclosures and operating electrical power. The careful calibration of thermal properties of materials used in the electrical systems, enrich the data bank of used materials. Parametric sweep were used to predict the thermal property of composite materials. The simulations of existing electrical systems within acceptable error tolerance create opportunities of predictive modeling of thermal profiles of new prototypes to improve the structural design (e.g. ensuring better thermal dissipation), reduce the likelihood of material failure due to overheating, predict the maximum rated power within acceptable operating temperature.
This research has been carried out in collaboration with

COMSOL Multiphysics has been used to numerically simulate the thermal behavior of various electrical cabinets under versatile environmental conditions. The fluid dynamics has been coupled with thermal conduction and radiation to capture the thermal properties of the electrical systems made of Glass Reinforced Plastic and Aluminum. Thermocouple sensors and thermographic camera were used to measure thermal profile of various electrical systems. Thermal simulation by COMSOL Multiphysics allowed a profound understanding of the internal physics. It has been observed that natural air convection, conductivity of enclosure material, and radiative surface plays a role in thermal dissipation depending on the sizes of enclosures and operating electrical power. The careful calibration of thermal properties of materials used in the electrical systems, enrich the data bank of used materials. Parametric sweep were used to predict the thermal property of composite materials. The simulations of existing electrical systems within acceptable error tolerance create opportunities of predictive modeling of thermal profiles of new prototypes to improve the structural design (e.g. ensuring better thermal dissipation), reduce the likelihood of material failure due to overheating, predict the maximum rated power within acceptable operating temperature.



This research has been carried out in collaboration with
 |
 |
